Chapter 7 Technician
The following was downloaded from http://www.ncvec.org/page.php?id=373 on 2023-04-01 by VE W3TM.
Modification of Public Release issued on March 7, 2022
4 Question Modifications:
T2A09 –replaced station’s with repeater’s in answer A to read: A. “CQ CQ” followed by the repeater’s call sign
2B12 - replaced answer A to read: A. Must match the repeater color code for access
T6B07 remove DC in answers A and B
T8D02 replaced digital with DMR before repeater in the question to read: What is a Talkgroup on a DMR repeater?
2022-2026 Technician Class Question Pool Errata
The following changes have been made to the posted 2022-2026 Technician Class FCC Element 2 Question Pool Released on January 17, 2022
Modification of Public Release issued on January 17, 2022
1 Question Deletion: T7D05 withdrawn from use
The remaining questions in T7D were not renumbered
Modification of Public Release issued on January 6, 2022
5 Question Modifications:
T4A07 replaced : (semi-colon) with . (period) in distractors
T5C08, T5D01, T5D02, T5DO3 reverted ‘V’ to ‘E’
2022-2026 Technician Class FCC Element 2 Question Pool Syllabus Effective 7/01/2022 – 6/30/2026
Summary
SUBELEMENT T1 COMMISSION’S RULES
[6 Exam Questions - 6 Groups] 67 Questions
T1A - Purpose and permissible use of the Amateur Radio Service; Operator/primary station license grant; Meanings of basic terms used in FCC rules; Interference; RACES rules; Phonetics; Frequency Coordinator
T1B - Frequency allocations; Emission modes; Spectrum sharing; Transmissions near band edges; Contacting the International Space Station; Power output
T1C - Licensing: classes, sequential and vanity call sign systems, places where the Amateur Radio Service is regulated by the FCC, name and address on FCC license database, term, renewal, grace period, maintaining mailing address; International communications
T1D - Authorized and prohibited transmissions: communications with other countries, music, exchange of information with other services, indecent language, compensation for operating, retransmission of other amateur signals, encryption, sale of equipment, unidentified transmissions, one-way transmission
T1E - control operator: eligibility, designating, privileges, duties, location, required; control point; Control types: automatic, remote
T1F - Station identification; Repeaters; Third party communications; Club stations; FCC inspection
SUBELEMENT T2 - OPERATING PROCEDURES
[3 Exam Questions - 3 Groups] 36 Questions
T2A - Station operation: choosing an operating frequency, calling another station, test transmissions; Band plans: calling frequencies, repeater offsets
T2B – VHF/UHF operating practices: FM repeater, simplex, reverse splits; Access tones: CTCSS, DTMF; DMR operation; Resolving operational problems; Q signals
T2C – Public service: emergency operations, applicability of FCC rules, RACES and ARES, net and traffic procedures, operating restrictions during emergencies, use of phonetics in message handling
SUBELEMENT T3 – RADIO WAVE PROPAGATION
– [3 Exam Questions - 3 Groups] 34 Questions
T3A - Radio wave characteristics: how a radio signal travels, fading, multipath, polarization, wavelength vs absorption; Antenna orientation
T3B - Electromagnetic wave properties: wavelength vs frequency, nature and velocity of electromagnetic waves, relationship of wavelength and frequency; Electromagnetic spectrum definitions: UHF, VHF, HF
T3C - Propagation modes: sporadic E, meteor scatter, auroral propagation, tropospheric ducting; F region skip; Line of sight and radio horizon
SUBELEMENT T4 – AMATEUR RADIO PRACTICES
– [2 Exam Questions - 2 Groups] 24 Questions
T4A – Station setup: connecting a microphone, a power source, a computer, digital equipment, an SWR meter; bonding; Mobile radio installation
T4B - Operating controls: frequency tuning, use of filters, squelch function, AGC, memory channels, noise blanker, microphone gain, receiver incremental tuning (RIT), bandwidth selection, digital transceiver configuration
SUBELEMENT T5 – ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES
– [4 Exam Questions - 4 Groups] 52 Questions
T5A – Current and voltage: terminology and units, conductors and insulators, alternating and direct current
T5B - Math for electronics: conversion of electrical units, decibels
T5C – Capacitance and inductance terminology and units; Radio frequency definition and units; Impedance definition and units; Calculating power
T5D – Ohm’s Law; Series and parallel circuits
SUBELEMENT T6 – ELECTRONIC AND ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
– [4 Exam Questions - 4 Groups] 47 Questions
T6A - Fixed and variable resistors; Capacitors; Inductors; Fuses; Switches; Batteries
T6B – Semiconductors: basic principles and applications of solid state devices, diodes and transistors
T6C - Circuit diagrams: use of schematics, basic structure; Schematic symbols of basic components
T6D - Component functions: rectifiers, relays, voltage regulators, meters, indicators, integrated circuits, transformers; Resonant circuit; Shielding
SUBELEMENT T7 – PRACTICAL CIRCUITS
– [4 Exam Questions - 4 Groups] 44 Questions
T7A – Station equipment: receivers, transceivers, transmitter amplifiers, receive amplifiers, transverters; Basic radio circuit concepts and terminology: sensitivity, selectivity, mixers, oscillators, PTT, modulation
T7B – Symptoms, causes, and cures of common transmitter and receiver problems: overload and overdrive, distortion, interference and consumer electronics, RF feedback T7C – Antenna and transmission line measurements and troubleshooting: measuring SWR, effects of high SWR, causes of feed line failures; Basic coaxial cable characteristics; Use of dummy loads when testing
T7D – Using basic test instruments: voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter; Soldering
SUBELEMENT T8 – SIGNALS AND EMISSIONS
– [4 Exam Questions - 4 Groups] 48 Questions
T8A – Basic characteristics of FM and SSB; Bandwidth of various modulation modes: CW, SSB, FM, fast-scan TV; Choice of emission type: selection of USB vs LSB, use of SSB for weak signal work, use of FM for VHF packet and repeaters
T8B - Amateur satellite operation: Doppler shift, basic orbits, operating protocols, modulation mode selection, transmitter power considerations, telemetry and telecommand, satellite tracking programs, beacons, uplink and downlink mode definitions, spin fading, definition of “LEO”, setting uplink power
T8C – Operating activities: radio direction finding, contests, linking over the internet, exchanging grid locators
T8D – Non-voice and digital communications: image signals and definition of [NTSC], CW, packet radio, PSK, APRS, error detection and correction, amateur radio networking, Digital Mobile Radio, WSJT modes, Broadband-Hamnet
SUBELEMENT T9 – ANTENNAS AND FEED LINES
- [2 Exam Questions - 2 Groups] 24 Questions
T9A – Antennas: vertical and horizontal polarization, concept of antenna gain, definition and types of beam antennas, antenna loading, common portable and mobile antennas, relationships between resonant length and frequency, dipole pattern
T9B – Feed lines: types, attenuation vs frequency, selecting; SWR concepts; Antenna tuners (couplers); RF Connectors: selecting, weather protection
SUBELEMENT T0 – SAFETY
– [3 Exam Questions - 3 Groups] 36 Questions
T0A – Power circuits and hazards: hazardous voltages, fuses and circuit breakers, grounding, electrical code compliance; Lightning protection; Battery safety
T0B – Antenna safety: tower safety and grounding, installing antennas, antenna supports
T0C - RF hazards: radiation exposure, proximity to antennas, recognized safe power levels, radiation types, duty cycle
Questions
SUBELEMENT T1 – COMMISSION’S RULES
- [6 Exam Questions - 6 Groups]
T1A
Purpose and permissible use of the Amateur Radio Service; Operator/primary station license grant; Meanings of basic terms used in FCC rules; Interference; RACES rules; Phonetics; Frequency Coordinator
T1A01 (C) [97.1]
Which of the following is part of the Basis and Purpose of the Amateur Radio Service?
A. Providing personal radio communications for as many citizens as possible B. Providing communications for international non-profit organizations C. Advancing skills in the technical and communication phases of the radio art D. All these choices are correct
T1A02 (C) [97.1]
Which agency regulates and enforces the rules for the Amateur Radio Service in the United States?
A. FEMA B. Homeland Security C. The FCC D. All these choices are correct
T1A03 (B) [97.119(b)(2)]
What do the FCC rules state regarding the use of a phonetic alphabet for station identification in the Amateur Radio Service?
A. It is required when transmitting emergency messages B. It is encouraged C. It is required when in contact with foreign stations D. All these choices are correct
T1A04 (A) [97.5(b)(1)]
How many operator/primary station license grants may be held by any one person?
A. One B. No more than two C. One for each band on which the person plans to operate D. One for each permanent station location from which the person plans to operate
T1A05 (C) [97.7]
What proves that the FCC has issued an operator/primary license grant?
A. A printed copy of the certificate of successful completion of examination B. An email notification from the NCVEC granting the license C. The license appears in the FCC ULS database D. All these choices are correct
T1A06 (D) [97.3(a)(9)]
What is the FCC Part 97 definition of a beacon?
A. A government transmitter marking the amateur radio band edges B. A bulletin sent by the FCC to announce a national emergency C. A continuous transmission of weather information authorized in the amateur bands by the National Weather Service D. An amateur station transmitting communications for the purposes of observing propagation or related experimental activities
T1A07 (C) [97.3(a)(41)]
What is the FCC Part 97 definition of a space station?
A. Any satellite orbiting Earth B. A manned satellite orbiting Earth C. An amateur station located more than 50 km above Earth’s surface D. An amateur station using amateur radio satellites for relay of signals
T1A08 (B) [97.3(a)(22)]
Which of the following entities recommends transmit/receive channels and other parameters for auxiliary and repeater stations?å
A. Frequency Spectrum Manager appointed by the FCC B. Volunteer Frequency Coordinator recognized by local amateurs C. FCC Regional Field Office D. International Telecommunication Union
T1A09 (C) [97.3(a)(22)]
Who selects a Frequency Coordinator?
A. The FCC Office of Spectrum Management and Coordination Policy B. The local chapter of the Office of National Council of Independent Frequency Coordinators C. Amateur operators in a local or regional area whose stations are eligible to be repeater or auxiliary stations D. FCC Regional Field Office
T1A10 (D) [97.3(a)(38), 97.407]
What is the Radio Amateur Civil Emergency Service (RACES)?
A. A radio service using amateur frequencies for emergency management or civil defense communications B. A radio service using amateur stations for emergency management or civil defense communications C. An emergency service using amateur operators certified by a civil defense organization as being enrolled in that organization D. All these choices are correct
T1A11 (B) [97.101 (d)]
When is willful interference to other amateur radio stations permitted?
A. To stop another amateur station that is breaking the FCC rules B. At no time C. When making short test transmissions D. At any time, stations in the Amateur Radio Service are not protected from willful interference
T1B
Frequency allocations; Emission modes; Spectrum sharing; Transmissions near band edges; Contacting the International Space Station; Power output
T1B01 (C) [97.301 (e)]
Which of the following frequency ranges are available for phone operation by Technician licensees?
A. 28.050 MHz to 28.150 MHz B. 28.100 MHz to 28.300 MHz C. 28.300 MHz to 28.500 MHz D. 28.500 MHz to 28.600 MHz
T1B02 (B) [97.301, 97.207(c)]
Which amateurs may contact the International Space Station (ISS) on VHF bands?
A. Any amateur holding a General class or higher license B. Any amateur holding a Technician class or higher license C. Any amateur holding a General class or higher license who has applied for and received approval from NASA D. Any amateur holding a Technician class or higher license who has applied for and received approval from NASA
T1B03 (B) [97.301(a)]
Which frequency is in the 6 meter amateur band?
A. 49.00 MHz B. 52.525 MHz C. 28.50 MHz D. 222.15 MHz
T1B04 (D) [97.301(a)]
Which amateur band includes 146.52 MHz?
A. 6 meters B. 20 meters C. 70 centimeters D. 2 meters
T1B05 (D) [97.305(c)]
How may amateurs use the 219 to 220 MHz segment of 1.25 meter band?
A. Spread spectrum only B. Fast-scan television only C. Emergency traffic only D. Fixed digital message forwarding systems only
T1B06 (B) [97.301(e), 97.305]
On which HF bands does a Technician class operator have phone privileges?
A. None B. 10 meter band only C. 80 meter, 40 meter, 15 meter, and 10 meter bands D. 30 meter band only
T1B07 (A) [97.305(a), (c)]
Which of the following VHF/UHF band segments are limited to CW only?
A. 50.0 MHz to 50.1 MHz and 144.0 MHz to 144.1 MHz B. 219 MHz to 220 MHz and 420.0 MHz to 420.1 MHz C. 902.0 MHz to 902.1 MHz D. All these choices are correct
T1B08 (A) [97.303]
How are US amateurs restricted in segments of bands where the Amateur Radio Service is secondary?
A. U.S. amateurs may find non-amateur stations in those segments, and must avoid interfering with them B. U.S. amateurs must give foreign amateur stations priority in those segments C. International communications are not permitted in those segments D. Digital transmissions are not permitted in those segments
T1B09 (D) [97.101(a), 97.301(a-e)]
Why should you not set your transmit frequency to be exactly at the edge of an amateur band or sub-band?
A. To allow for calibration error in the transmitter frequency display B. So that modulation sidebands do not extend beyond the band edge C. To allow for transmitter frequency drift D. All these choices are correct
T1B10 (C) [97.305(c)]
Where may SSB phone be used in amateur bands above 50 MHz?
A. Only in sub-bands allocated to General class or higher licensees B. Only on repeaters C. In at least some segment of all these bands D. On any band if the power is limited to 25 watts
T1B11 (A) [97.313]
What is the maximum peak envelope power output for Technician class operators in their HF band segments?
A. 200 watts B. 100 watts C. 50 watts D. 10 watts
T1B12 (D) [97.313(b)]
Except for some specific restrictions, what is the maximum peak envelope power output for Technician class operators using frequencies above 30 MHz?
A. 50 watts B. 100 watts C. 500 watts D. 1500 watts
T1C
Licensing: classes, sequential and vanity call sign systems, places where the Amateur Radio Service is regulated by the FCC, name and address on FCC license database, term, renewal, grace period, maintaining mailing address; International communications
T1C01 (D) [97.9(a), 97.17(a)]
For which license classes are new licenses currently available from the FCC?
A. Novice, Technician, General, Amateur Extra B. Technician, Technician Plus, General, Amateur Extra C. Novice, Technician Plus, General, Advanced D. Technician, General, Amateur Extra
T1C02 (D) [97.19]
Who may select a desired call sign under the vanity call sign rules?
A. Only a licensed amateur with a General or Amateur Extra Class license B. Only a licensed amateur with an Amateur Extra Class license C. Only a licensed amateur who has been licensed continuously for more than 10 years D. Any licensed amateur
T1C03 (A) [97.117]
What types of international communications are an FCC-licensed amateur radio station permitted to make?
A. Communications incidental to the purposes of the Amateur Radio Service and remarks of a personal character B. Communications incidental to conducting business or remarks of a personal nature C. Only communications incidental to contest exchanges; all other communications are prohibited D. Any communications that would be permitted by an international broadcast station
T1C04 (B) [97.23]
What may happen if the FCC is unable to reach you by email?
A. Fine and suspension of operator license B. Revocation of the station license or suspension of the operator license C. Revocation of access to the license record in the FCC system D. Nothing; there is no such requirement
T1C05 (A)
Which of the following is a valid Technician class call sign format?
A. KF1XXX B. KA1X C. W1XX D. All these choices are correct
T1C06 (D) [97.5(a)(2)]
From which of the following locations may an FCC-licensed amateur station transmit?
A. From within any country that belongs to the International Telecommunication Union B. From within any country that is a member of the United Nations C. From anywhere within International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Regions 2 and 3 D. From any vessel or craft located in international waters and documented or registered in the United States
T1C07 (B) [97.23]
Which of the following can result in revocation of the station license or suspension of the operator license?
A. Failure to inform the FCC of any changes in the amateur station following performance of an RF safety environmental evaluation B. Failure to provide and maintain a correct email address with the FCC C. Failure to obtain FCC type acceptance prior to using a home-built transmitter D. Failure to have a copy of your license available at your station
T1C08 (C) [97.25]
What is the normal term for an FCC-issued amateur radio license?
A. Five years B. Life C. Ten years D. Eight years
T1C09 (A) [97.21(a)(b)]
What is the grace period for renewal if an amateur license expires?
A. Two years B. Three years C. Five years D. Ten years
T1C10 (C) [97.5a]
How soon after passing the examination for your first amateur radio license may you transmit on the amateur radio bands?
A. Immediately on receiving your Certificate of Successful Completion of Examination (CSCE) B. As soon as your operator/station license grant appears on the ARRL website C. As soon as your operator/station license grant appears in the FCC’s license database D. As soon as you receive your license in the mail from the FCC
T1C11 (D) [97.21(b)]
If your license has expired and is still within the allowable grace period, may you continue to transmit on the amateur radio bands?
A. Yes, for up to two years B. Yes, as soon as you apply for renewal C. Yes, for up to one year D. No, you must wait until the license has been renewed
T1D
Authorized and prohibited transmissions: communications with other countries, music, exchange of information with other services, indecent language, compensation for operating, retransmission of other amateur signals, encryption, sale of equipment, unidentified transmissions, one-way transmission
T1D01 (A) [97.111(a)(1)]
With which countries are FCC-licensed amateur radio stations prohibited from exchanging communications?
A. Any country whose administration has notified the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) that it objects to such communications B. Any country whose administration has notified the American Radio Relay League (ARRL) that it objects to such communications C. Any country banned from such communications by the International Amateur Radio Union (IARU) D. Any country banned from making such communications by the American Radio Relay League (ARRL)
T1D02 (B) [97.113(b), 97.111(b)]
Under which of the following circumstances are one-way transmissions by an amateur station prohibited?
A. In all circumstances B. Broadcasting C. International Morse Code Practice D. Telecommand or transmissions of telemetry
T1D03 (C) [97.211(b), 97.215(b), 97.113(a)(4)]
When is it permissible to transmit messages encoded to obscure their meaning?
A. Only during contests B. Only when transmitting certain approved digital codes C. Only when transmitting control commands to space stations or radio control craft D. Never
T1D04 (A) [97.113(a)(4), 97.113(c)]
Under what conditions is an amateur station authorized to transmit music using a phone emission?
A. When incidental to an authorized retransmission of manned spacecraft communications B. When the music produces no spurious emissions C. When transmissions are limited to less than three minutes per hour D. When the music is transmitted above 1280 MHz
T1D05 (D) [97.113(a)(3)(ii)]
When may amateur radio operators use their stations to notify other amateurs of the availability of equipment for sale or trade?
A. Never B. When the equipment is not the personal property of either the station licensee, or the control operator, or their close relatives C. When no profit is made on the sale D. When selling amateur radio equipment and not on a regular basis
T1D06 (B) [97.113(a)(4)]
What, if any, are the restrictions concerning transmission of language that may be considered indecent or obscene?
A. The FCC maintains a list of words that are not permitted to be used on amateur frequencies B. Any such language is prohibited C. The ITU maintains a list of words that are not permitted to be used on amateur frequencies D. There is no such prohibition
T1D07 (D) [97.113(d)]
What types of amateur stations can automatically retransmit the signals of other amateur stations?
A. Auxiliary, beacon, or Earth stations B. Earth, repeater, or space stations C. Beacon, repeater, or space stations D. Repeater, auxiliary, or space stations
T1D08 (B) [97.113(a)(3)(iii)]
In which of the following circumstances may the control operator of an amateur station receive compensation for operating that station?
A. When the communication is related to the sale of amateur equipment by the control operator’s employer B. When the communication is incidental to classroom instruction at an educational institution C. When the communication is made to obtain emergency information for a local broadcast station D. All these choices are correct
T1D09 (A) [97.113(5)(b)]
When may amateur stations transmit information in support of roadcasting, program production, or news gathering, assuming no other means is available?
A. When such communications are directly related to the immediate safety of human life or protection of property B. When roadcasting communications to or from the space shuttle C. Where noncommercial programming is gathered and supplied exclusively to the National Public Radio network D. Never
T1D10 (D) [97.3(a)(10)]
How does the FCC define broadcasting for the Amateur Radio Service?
A. Two-way transmissions by amateur stations B. Any transmission made by the licensed station C. Transmission of messages directed only to amateur operators D. Transmissions intended for reception by the general public
T1D11 (D) [97.119(a)]
When may an amateur station transmit without identifying on the air?
A. When the transmissions are of a brief nature to make station adjustments B. When the transmissions are unmodulated C. When the transmitted power level is below 1 watt D. When transmitting signals to control model craft
T1E
Control operator: eligibility, designating, privileges, duties, location, required; Control point; Control types: automatic, remote.
T1E01 (D) [97.7(a)]
When may an amateur station transmit without a control operator?
A. When using automatic control, such as in the case of a repeater B. When the station licensee is away and another licensed amateur is using the station C. When the transmitting station is an auxiliary station D. Never
T1E02 (D) [97.301, 97.207(c)]
Who may be the control operator of a station communicating through an amateur satellite or space station?
A. Only an Amateur Extra Class operator B. A General class or higher licensee with a satellite operator certification C. Only an Amateur Extra Class operator who is also an AMSAT member D. Any amateur allowed to transmit on the satellite uplink frequency
T1E03 (A) [97.103(b)]
Who must designate the station control operator?
A. The station licensee B. The FCC C. The frequency coordinator D. Any licensed operator
T1E04 (D) [97.103(b)]
What determines the transmitting frequency privileges of an amateur station?
A. The frequency authorized by the frequency coordinator B. The frequencies printed on the license grant C. The highest class of operator license held by anyone on the premises D. The class of operator license held by the control operator
T1E05 (C) [97.3(a)(14)]
What is an amateur station’s control point?
A. The location of the station’s transmitting antenna B. The location of the station’s transmitting apparatus C. The location at which the control operator function is performed D. The mailing address of the station licensee
T1E06 (A) [97.301]
When, under normal circumstances, may a Technician class licensee be the control operator of a station operating in an Amateur Extra Class band segment?
A. At no time B. When designated as the control operator by an Amateur Extra Class licensee C. As part of a multi-operator contest team D. When using a club station whose trustee holds an Amateur Extra Class license
T1E07 (D) [97.103(a)]
When the control operator is not the station licensee, who is responsible for the proper operation of the station?
A. All licensed amateurs who are present at the operation B. Only the station licensee C. Only the control operator D. The control operator and the station licensee
T1E08 (A) [97.3(a)(6), 97.205(d)]
Which of the following is an example of automatic control?
A. Repeater operation B. Controlling a station over the internet C. Using a computer or other device to send CW automatically D. Using a computer or other device to identify automatically
T1E09 (D) [97.109(c)]
Which of the following are required for remote control operation?
A. The control operator must be at the control point B. A control operator is required at all times C. The control operator must indirectly manipulate the controls D. All these choices are correct
T1E10 (B) [97.3(a)(39)]
Which of the following is an example of remote control as defined in Part 97?
A. Repeater operation B. Operating the station over the internet C. Controlling a model aircraft, boat, or car by amateur radio D. All these choices are correct
T1E11 (D) [97.103(a)]
Who does the FCC presume to be the control operator of an amateur station, unless documentation to the contrary is in the station records?
A. The station custodian B. The third party participant C. The person operating the station equipment D. The station licensee
T1F
Station identification; Repeaters; Third party communications; Club stations; FCC inspection
T1F01 (B) [97.103(c)]
When must the station and its records be available for FCC inspection?
A. At any time ten days after notification by the FCC of such an inspection B. At any time upon request by an FCC representative C. At any time after written notification by the FCC of such inspection D. Only when presented with a valid warrant by an FCC official or government agent
T1F02 (C) [97.119 (a)]
How often must you identify with your FCC-assigned call sign when using tactical call signs such as “Race Headquarters”?
A. Never, the tactical call is sufficient B. Once during every hour C. At the end of each communication and every ten minutes during a communication D. At the end of every transmission
T1F03 (D) [97.119(a)]
When are you required to transmit your assigned call sign?
A. At the beginning of each contact, and every 10 minutes thereafter B. At least once during each transmission C. At least every 15 minutes during and at the end of a communication D. At least every 10 minutes during and at the end of a communication
T1F04 (C) [97.119(b)(2)]
What language may you use for identification when operating in a phone sub-band?
A. Any language recognized by the United Nations B. Any language recognized by the ITU C. English D. English, French, or Spanish
T1F05 (B) [97.119(b)(2)]
What method of call sign identification is required for a station transmitting phone signals?
A. Send the call sign followed by the indicator RPT B. Send the call sign using a CW or phone emission C. Send the call sign followed by the indicator R D. Send the call sign using only a phone emission
T1F06 (D) [97.119(c)]
Which of the following self-assigned indicators are acceptable when using a phone transmission?
A. KL7CC stroke W3 B. KL7CC slant W3 C. KL7CC slash W3 D. All these choices are correct
T1F07 (B) [97.115(a)(2)]
Which of the following restrictions apply when a non-licensed person is allowed to speak to a foreign station using a station under the control of a licensed amateur operator?
A. The person must be a U.S. citizen B. The foreign station must be in a country with which the U.S. has a third party agreement C. The licensed control operator must do the station identification D. All these choices are correct
T1F08 (A) [97.3(a)(47)]
What is the definition of third party communications?
A. A message from a control operator to another amateur station control operator on behalf of another person B. Amateur radio communications where three stations are in communications with one another C. Operation when the transmitting equipment is licensed to a person other than the control operator D. Temporary authorization for an unlicensed person to transmit on the amateur bands for technical experiments
T1F09 (C) [97.3(a)(40)]
What type of amateur station simultaneously retransmits the signal of another amateur station on a different channel or channels?
A. Beacon station B. Earth station C. Repeater station D. Message forwarding station
T1F10 (A) [97.205(g)]
Who is accountable if a repeater inadvertently retransmits communications that violate the FCC rules?
A. The control operator of the originating station B. The control operator of the repeater C. The owner of the repeater D. Both the originating station and the repeater owner
T1F11 (B) [97.5(b)(2)]
Which of the following is a requirement for the issuance of a club station license grant?
A. The trustee must have an Amateur Extra Class operator license grant B. The club must have at least four members C. The club must be registered with the American Radio Relay League D. All these choices are correct
SUBELEMENT T2 - OPERATING PROCEDURES
- [3 Exam Questions - 3 Groups]
T2A
Station operation: choosing an operating frequency, calling another station, test transmissions; Band plans: calling frequencies, repeater offsets
T2A01 (B)
What is a common repeater frequency offset in the 2 meter band?
A. Plus or minus 5 MHz B. Plus or minus 600 kHz C. Plus or minus 500 kHz D. Plus or minus 1 MHz
T2A02 (A)
What is the national calling frequency for FM simplex operations in the 2 meter band?
A. 146.520 MHz B. 145.000 MHz C. 432.100 MHz D. 446.000 MHz
T2A03 (A)
What is a common repeater frequency offset in the 70 cm band?
A. Plus or minus 5 MHz B. Plus or minus 600 kHz C. Plus or minus 500 kHz D. Plus or minus 1 MHz
T2A04 (B)
What is an appropriate way to call another station on a repeater if you know the other station’s call sign?
A. Say “break, break,” then say the station’s call sign B. Say the station’s call sign, then identify with your call sign C. Say “CQ” three times, then the other station’s call sign D. Wait for the station to call CQ, then answer
T2A05 (C)
How should you respond to a station calling CQ?
A. Transmit “CQ” followed by the other station’s call sign B. Transmit your call sign followed by the other station’s call sign C. Transmit the other station’s call sign followed by your call sign D. Transmit a signal report followed by your call sign
T2A06 (A)
Which of the following is required when making on-the-air test transmissions?
A. Identify the transmitting station B. Conduct tests only between 10 p.m. and 6 a.m. local time C. Notify the FCC of the transmissions D. All these choices are correct
T2A07 (A)
What is meant by “repeater offset”?
A. The difference between a repeater’s transmit and receive frequencies B. The repeater has a time delay to prevent interference C. The repeater station identification is done on a separate frequency D. The number of simultaneous transmit frequencies used by a repeater
T2A08 (D)
What is the meaning of the procedural signal “CQ”?
A. Call on the quarter hour B. Test transmission, no reply expected C. Only the called station should transmit D. Calling any station
T2A09 (B)
Which of the following indicates that a station is listening on a repeater and looking for a contact?
A. “CQ CQ” followed by the repeater’s call sign B. The station’s call sign followed by the word “monitoring” C. The repeater call sign followed by the station’s call sign D. “[QSY]” followed by your call sign
T2A10 (A)
What is a band plan, beyond the privileges established by the FCC?
A. A voluntary guideline for using different modes or activities within an amateur band B. A list of operating schedules C. A list of available net frequencies D. A plan devised by a club to indicate frequency band usage
T2A11 (C)
What term describes an amateur station that is transmitting and receiving on the same frequency?
A. Full duplex B. Diplex C. Simplex D. Multiplex
T2A12 (D)
What should you do before calling CQ?
A. Listen first to be sure that no one else is using the frequency B. Ask if the frequency is in use C. Make sure you are authorized to use that frequency D. All these choices are correct
T2B
VHF/UHF operating practices: FM repeater, simplex, reverse splits; Access tones: CTCSS, DTMF; DMR operation; Resolving operational problems; Q signals ##### T2B01 (C) {- #T2B01}
How is a VHF/UHF transceiver’s “reverse” function used?
A. To reduce power output B. To increase power output C. To listen on a repeater’s input frequency D. To listen on a repeater’s output frequency
T2B02 (D)
What term describes the use of a sub-audible tone transmitted along with normal voice audio to open the squelch of a receiver?
T2B03 (A)
Which of the following describes a linked repeater network?
A. A network of repeaters in which signals received by one repeater are transmitted by all the repeaters in the network B. A single repeater with more than one receiver C. Multiple repeaters with the same control operator D. A system of repeaters linked by APRS
T2B04 (D)
Which of the following could be the reason you are unable to access a repeater whose output you can hear?
A. Improper transceiver offset B. You are using the wrong CTCSS tone C. You are using the wrong DCS code D. All these choices are correct
T2B05 (C)
What would cause your FM transmission audio to be distorted on voice peaks?
A. Your repeater offset is inverted B. You need to talk louder C. You are talking too loudly D. Your transmit power is too high
T2B07 (C)
How can you join a digital repeater’s “talkgroup”?
A. Register your radio with the local FCC office B. Join the repeater owner’s club C. Program your radio with the group’s ID or code D. Sign your call after the courtesy tone
T2B08 (A)
Which of the following applies when two stations transmitting on the same frequency interfere with each other?
A. The stations should negotiate continued use of the frequency B. Both stations should choose another frequency to avoid conflict C. Interference is inevitable, so no action is required D. Use subaudible tones so both stations can share the frequency
T2B09 (A)
Why are simplex channels designated in the VHF/UHF band plans?
A. So stations within range of each other can communicate without tying up a repeater B. For contest operation C. For working DX only D. So stations with simple transmitters can access the repeater without automated offset
T2B12 (A)
What is the purpose of the color code used on DMR repeater systems?
A. Must match the repeater color code for access B. Defines the frequency pair to use C. Identifies the codec used D. Defines the minimum signal level required for access
T2B13 (B)
What is the purpose of a squelch function?
A. Reduce a CW transmitter’s key clicks B. Mute the receiver audio when a signal is not present C. Eliminate parasitic oscillations in an RF amplifier D. Reduce interference from impulse noise
T2C
Public service: emergency operations, applicability of FCC rules, RACES and [ARES], net and traffic procedures, operating restrictions during emergencies, use of phonetics in message handling
T2C01 (D) [97.103(a)]
When do FCC rules NOT apply to the operation of an amateur station?
A. When operating a RACES station B. When operating under special FEMA rules C. When operating under special [ARES] rules D. FCC rules always apply
T2C02 (C)
Which of the following are typical duties of a Net Control Station?
A. Choose the regular net meeting time and frequency B. Ensure that all stations checking into the net are properly licensed for operation on the net frequency C. Call the net to order and direct communications between stations checking in D. All these choices are correct
T2C03 (C)
What technique is used to ensure that voice messages containing unusual words are received correctly?
A. Send the words by voice and Morse code B. Speak very loudly into the microphone C. Spell the words using a standard phonetic alphabet D. All these choices are correct
T2C04 (D)
What is RACES?
A. An emergency organization combining amateur radio and citizens band operators and frequencies B. An international radio experimentation society C. A radio contest held in a short period, sometimes called a “sprint” D. An FCC part 97 Amateur Radio Service for civil defense communications during national emergencies
T2C05 (A)
What does the term “traffic” refer to in net operation?
A. Messages exchanged by net stations B. The number of stations checking in and out of a net C. Operation by mobile or portable stations D. Requests to activate the net by a served agency
T2C06 (A)
What is the Amateur Radio Emergency Service ([ARES])?
A. A group of licensed amateurs who have voluntarily registered their qualifications and equipment for communications duty in the public service B. A group of licensed amateurs who are members of the military and who voluntarily agreed to provide message handling services in the case of an emergency C. A training program that provides licensing courses for those interested in obtaining an amateur license to use during emergencies D. A training program that certifies amateur operators for membership in the Radio Amateur Civil Emergency Service
T2C07 (C)
Which of the following is standard practice when you participate in a net?
A. When first responding to the net control station, transmit your call sign, name, and address as in the FCC database B. Record the time of each of your transmissions C. Unless you are reporting an emergency, transmit only when directed by the net control station D. All these choices are correct
T2C08 (A)
Which of the following is a characteristic of good traffic handling?
A. Passing messages exactly as received B. Making decisions as to whether messages are worthy of relay or delivery C. Ensuring that any newsworthy messages are relayed to the news media D. All these choices are correct
T2C09 (D)
Are amateur station control operators ever permitted to operate outside the frequency privileges of their license class?
A. No B. Yes, but only when part of a FEMA emergency plan C. Yes, but only when part of a RACES emergency plan D. Yes, but only in situations involving the immediate safety of human life or protection of property
T2C10 (D)
What information is contained in the preamble of a formal traffic message?
A. The email address of the originating station B. The address of the intended recipient C. The telephone number of the addressee D. Information needed to track the message
T2C11 (A)
What is meant by “check” in a radiogram header?
A. The number of words or word equivalents in the text portion of the message B. The call sign of the originating station C. A list of stations that have relayed the message D. A box on the message form that indicates that the message was received and/or relayed
SUBELEMENT T3 – RADIO WAVE PROPAGATION
– [3 Exam Questions - 3 Groups]
T3A
Radio wave characteristics: how a radio signal travels, fading, multipath, polarization, wavelength vs absorption; Antenna orientation
T3A01 (C)
Why do VHF signal strengths sometimes vary greatly when the antenna is moved only a few feet?
A. The signal path encounters different concentrations of water vapor B. VHF ionospheric propagation is very sensitive to path length C. Multipath propagation cancels or reinforces signals D. All these choices are correct
T3A02 (B)
What is the effect of vegetation on UHF and microwave signals?
A. Knife-edge diffraction B. Absorption C. Amplification D. Polarization rotation
T3A03 (C)
What antenna polarization is normally used for long-distance CW and SSB contacts on the VHF and UHF bands?
A. Right-hand circular B. Left-hand circular C. Horizontal D. Vertical
T3A04 (B)
What happens when antennas at opposite ends of a VHF or UHF line of sight radio link are not using the same polarization?
A. The modulation sidebands might become inverted B. Received signal strength is reduced C. Signals have an echo effect D. Nothing significant will happen
T3A05 (B)
When using a directional antenna, how might your station be able to communicate with a distant repeater if buildings or obstructions are blocking the direct line of sight path?
A. Change from vertical to horizontal polarization B. Try to find a path that reflects signals to the repeater C. Try the long path D. Increase the antenna SWR
T3A06 (B)
What is the meaning of the term “picket fencing”?
A. Alternating transmissions during a net operation B. Rapid flutter on mobile signals due to multipath propagation C. A type of ground system used with vertical antennas D. Local vs long-distance communications
T3A07 (C)
What weather condition might decrease range at microwave frequencies?
A. High winds B. Low barometric pressure C. Precipitation D. Colder temperatures
T3A08 (D)
What is a likely cause of irregular fading of signals propagated by the ionosphere?
A. Frequency shift due to Faraday rotation B. Interference from thunderstorms C. Intermodulation distortion D. Random combining of signals arriving via different paths
T3A09 (B)
Which of the following results from the fact that signals propagated by the ionosphere are elliptically polarized?
A. Digital modes are unusable B. Either vertically or horizontally polarized antennas may be used for transmission or reception C. FM voice is unusable D. Both the transmitting and receiving antennas must be of the same polarization
T3A10 (D)
What effect does multi-path propagation have on data transmissions?
A. Transmission rates must be increased by a factor equal to the number of separate paths observed B. Transmission rates must be decreased by a factor equal to the number of separate paths observed C. No significant changes will occur if the signals are transmitted using FM D. Error rates are likely to increase
T3B
Electromagnetic wave properties: wavelength vs frequency, nature and velocity of electromagnetic waves, relationship of wavelength and frequency; Electromagnetic spectrum definitions: UHF, VHF, HF
T3B01 (D)
What is the relationship between the electric and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave?
A. They travel at different speeds B. They are in parallel C. They revolve in opposite directions D. They are at right angles
T3B02 (A)
What property of a radio wave defines its polarization?
A. The orientation of the electric field B. The orientation of the magnetic field C. The ratio of the energy in the magnetic field to the energy in the electric field D. The ratio of the velocity to the wavelength
T3B03 (C)
What are the two components of a radio wave?
A. Impedance and reactance B. Voltage and current C. Electric and magnetic fields D. Ionizing and non-ionizing radiation
T3B04 (A)
What is the velocity of a radio wave traveling through free space?
A. Speed of light B. Speed of sound C. Speed inversely proportional to its wavelength D. Speed that increases as the frequency increases
T3B05 (B)
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
A. Wavelength gets longer as frequency increases B. Wavelength gets shorter as frequency increases C. Wavelength and frequency are unrelated D. Wavelength and frequency increase as path length increases
T3B06 (D)
What is the formula for converting frequency to approximate wavelength in meters?
A. Wavelength in meters equals frequency in hertz multiplied by 300 B. Wavelength in meters equals frequency in hertz divided by 300 C. Wavelength in meters equals frequency in megahertz divided by 300 D. Wavelength in meters equals 300 divided by frequency in megahertz
T3B07 (A)
In addition to frequency, which of the following is used to identify amateur radio bands?
A. The approximate wavelength in meters B. Traditional letter/number designators C. Channel numbers D. All these choices are correct
T3B08 (B)
What frequency range is referred to as VHF?
A. 30 kHz to 300 kHz B. 30 MHz to 300 MHz C. 300 kHz to 3000 kHz D. 300 MHz to 3000 MHz
T3B09 (D)
What frequency range is referred to as UHF?
A. 30 to 300 kHz B. 30 to 300 MHz C. 300 to 3000 kHz D. 300 to 3000 MHz
T3B10 (C)
What frequency range is referred to as HF?
A. 300 to 3000 MHz B. 30 to 300 MHz C. 3 to 30 MHz D. 300 to 3000 kHz
T3C
Propagation modes: sporadic E, meteor scatter, auroral propagation, tropospheric ducting; F region skip; Line of sight and radio horizon
T3C01 (C)
Why are simplex UHF signals rarely heard beyond their radio horizon?
A. They are too weak to go very far B. FCC regulations prohibit them from going more than 50 miles C. UHF signals are usually not propagated by the ionosphere D. UHF signals are absorbed by the ionospheric D region
T3C02 (C)
What is a characteristic of HF communication compared with communications on VHF and higher frequencies?
A. HF antennas are generally smaller B. HF accommodates wider bandwidth signals C. Long-distance ionospheric propagation is far more common on HF D. There is less atmospheric interference (static) on HF
T3C03 (B)
What is a characteristic of VHF signals received via auroral backscatter?
A. They are often received from 10,000 miles or more B. They are distorted and signal strength varies considerably C. They occur only during winter nighttime hours D. They are generally strongest when your antenna is aimed west
T3C04 (B)
Which of the following types of propagation is most commonly associated with occasional strong signals on the 10, 6, and 2 meter bands from beyond the radio horizon?
A. Backscatter B. Sporadic E C. D region absorption D. Gray-line propagation
T3C05 (A)
Which of the following effects may allow radio signals to travel beyond obstructions between the transmitting and receiving stations?
A. Knife-edge diffraction B. Faraday rotation C. Quantum tunneling D. Doppler shift
T3C06 (A)
What type of propagation is responsible for allowing over-the-horizon VHF and UHF communications to ranges of approximately 300 miles on a regular basis?
A. Tropospheric ducting B. D region refraction C. F2 region refraction D. Faraday rotation
T3C07 (B)
What band is best suited for communicating via meteor scatter?
A. 33 centimeters B. 6 meters C. 2 meters D. 70 centimeters
T3C08 (D)
What causes tropospheric ducting?
A. Discharges of lightning during electrical storms B. Sunspots and solar flares C. Updrafts from hurricanes and tornadoes D. Temperature inversions in the atmosphere
T3C09 (A)
What is generally the best time for long-distance 10 meter band propagation via the F region?
A. From dawn to shortly after sunset during periods of high sunspot activity B. From shortly after sunset to dawn during periods of high sunspot activity C. From dawn to shortly after sunset during periods of low sunspot activity D. From shortly after sunset to dawn during periods of low sunspot activity
T3C10 (A)
Which of the following bands may provide long-distance communications via the ionosphere’s F region during the peak of the sunspot cycle?
A. 6 and 10 meters B. 23 centimeters C. 70 centimeters and 1.25 meters D. All these choices are correct
T3C11 (C)
Why is the radio horizon for VHF and UHF signals more distant than the visual horizon?
A. Radio signals move somewhat faster than the speed of light B. Radio waves are not blocked by dust particles C. The atmosphere refracts radio waves slightly D. Radio waves are blocked by dust particles
SUBELEMENT T4 – AMATEUR RADIO PRACTICES
– [2 Exam Questions - 2 Groups]
T4A
Station setup: connecting a microphone, a power source, a computer, digital equipment, an SWR meter; bonding; Mobile radio installation
T4A01 (D)
Which of the following is an appropriate power supply rating for a typical 50 watt output mobile FM transceiver?
A. 24.0 volts at 4 amperes B. 13.8 volts at 4 amperes C. 24.0 volts at 12 amperes D. 13.8 volts at 12 amperes
T4A02 (A)
Which of the following should be considered when selecting an accessory SWR meter?
A. The frequency and power level at which the measurements will be made B. The distance that the meter will be located from the antenna C. The types of modulation being used at the station D. All these choices are correct
T4A03 (A)
Why are short, heavy-gauge wires used for a transceiver’s DC power connection?
A. To minimize voltage drop when transmitting B. To provide a good counterpoise for the antenna C. To avoid RF interference D. All these choices are correct
T4A04 (B)
How are the transceiver audio input and output connected in a station configured to operate using FT8?
A. To a computer running a terminal program and connected to a terminal node controller unit B. To the audio input and output of a computer running WSJT-X software C. To an FT8 conversion unit, a keyboard, and a computer monitor D. To a computer connected to the FT8converter.com website
T4A05 (A)
Where should an RF power meter be installed?
A. In the feed line, between the transmitter and antenna B. At the power supply output C. In parallel with the push-to-talk line and the antenna D. In the power supply cable, as close as possible to the radio
T4A06 (C)
What signals are used in a computer-radio interface for digital mode operation?
A. Receive and transmit mode, status, and location B. Antenna and RF power C. Receive audio, transmit audio, and transmitter keying D. NMEA GPS location and DC power
T4A07 (C)
Which of the following connections is made between a computer and a transceiver to use computer software when operating digital modes?
A. Computer “line out” to transceiver push-to-talk B. Computer “line in” to transceiver push-to-talk C. Computer “line in” to transceiver speaker connector D. Computer “line out” to transceiver speaker connector
T4A08 (D)
Which of the following conductors is preferred for bonding at RF?
A. Copper braid removed from coaxial cable B. Steel wire C. Twisted-pair cable D. Flat copper strap
T4A09 (B)
How can you determine the length of time that equipment can be powered from a battery?
A. Divide the watt-hour rating of the battery by the peak power consumption of the equipment B. Divide the battery ampere-hour rating by the average current draw of the equipment C. Multiply the watts per hour consumed by the equipment by the battery power rating D. Multiply the square of the current rating of the battery by the input resistance of the equipment
T4A10 (A)
What function is performed with a transceiver and a digital mode hot spot?
A. Communication using digital voice or data systems via the internet B. FT8 digital communications via AFSK C. RTTY encoding and decoding without a computer D. High-speed digital communications for meteor scatter
T4B
Operating controls: frequency tuning, use of filters, squelch function, AGC, memory channels, noise blanker, microphone gain, receiver incremental tuning (RIT), bandwidth selection, digital transceiver configuration
T4B01 (B)
What is the effect of excessive microphone gain on SSB transmissions?
A. Frequency instability B. Distorted transmitted audio C. Increased SWR D. All these choices are correct
T4B02 (A)
Which of the following can be used to enter a transceiver’s operating frequency?
A. The keypad or VFO knob B. The CTCSS or DTMF encoder C. The Automatic Frequency Control D. All these choices are correct
T4B03 (A)
How is squelch adjusted so that a weak FM signal can be heard?
A. Set the squelch threshold so that receiver output audio is on all the time B. Turn up the audio level until it overcomes the squelch threshold C. Turn on the anti-squelch function D. Enable squelch enhancement
T4B04 (B)
What is a way to enable quick access to a favorite frequency or channel on your transceiver?
A. Enable the frequency offset B. Store it in a memory channel C. Enable the VOX D. Use the scan mode to select the desired frequency
T4B05 (C)
What does the scanning function of an FM transceiver do?
A. Checks incoming signal deviation B. Prevents interference to nearby repeaters C. Tunes through a range of frequencies to check for activity D. Checks for messages left on a digital bulletin board
T4B06 (D)
Which of the following controls could be used if the voice pitch of a single-sideband signal returning to your CQ call seems too high or low?
A. The AGC or limiter B. The bandwidth selection C. The tone squelch D. The RIT or Clarifier
T4B07 (B)
What does a DMR “code plug” contain?
A. Your call sign in CW for automatic identification B. Access information for repeaters and talkgroups C. The codec for digitizing audio D. The DMR software version
T4B08 (B)
What is the advantage of having multiple receive bandwidth choices on a multimode transceiver?
A. Permits monitoring several modes at once by selecting a separate filter for each mode B. Permits noise or interference reduction by selecting a bandwidth matching the mode C. Increases the number of frequencies that can be stored in memory D. Increases the amount of offset between receive and transmit frequencies
T4B09 (C)
How is a specific group of stations selected on a digital voice transceiver?
A. By retrieving the frequencies from transceiver memory B. By enabling the group’s CTCSS tone C. By entering the group’s identification code D. By activating automatic identification
T4B10 (C)
Which of the following receiver filter bandwidths provides the best signal-to-noise ratio for SSB reception?
A. 500 Hz B. 1000 Hz C. 2400 Hz D. 5000 Hz
SUBELEMENT T5 – ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES
– [4 Exam Questions - 4 Groups]
:::
:::
T5A
Current and voltage: terminology and units, conductors and insulators, alternating and direct current
T5A01 (D)
Electrical current is measured in which of the following units?
A. Volts B. Watts C. Ohms D. Amperes
T5A02 (B)
Electrical power is measured in which of the following units?
A. Volts B. Watts C. Watt-hours D. Amperes
T5A03 (D)
What is the name for the flow of electrons in an electric circuit?
A. Voltage B. Resistance C. Capacitance D. Current
T5A05 (A)
What is the electrical term for the force that causes electron flow?
A. Voltage B. Ampere-hours C. Capacitance D. Inductance
T5A07 (B)
Why are metals generally good conductors of electricity?
A. They have relatively high density B. They have many free electrons C. They have many free protons D. All these choices are correct
T5A08 (B)
Which of the following is a good electrical insulator?
A. Copper B. Glass C. Aluminum D. Mercury
T5A09 (C)
Which of the following describes alternating current? A. Current that alternates between a positive direction and zero B. Current that alternates between a negative direction and zero C. Current that alternates between positive and negative directions D. All these answers are correct
T5A10 (C)
Which term describes the rate at which electrical energy is used?
A. Resistance B. Current C. Power D. Voltage
T5B
Math for electronics: conversion of electrical units, decibels
T5B01 (C)
How many milliamperes is 1.5 amperes?
A. 15 milliamperes B. 150 milliamperes C. 1500 milliamperes D. 15,000 milliamperes
T5B03 (C)
Which is equal to one kilovolt?
A. One one-thousandth of a volt B. One hundred volts C. One thousand volts D. One million volts
T5B04 (A)
Which is equal to one microvolt?
A. One one-millionth of a volt B. One million volts C. One thousand kilovolts D. One one-thousandth of a volt
T5B06 (D)
Which is equal to 3000 milliamperes?
A. 0.003 amperes B. 0.3 amperes C. 3,000,000 amperes D. 3 amperes
T5B08 (B)
Which is equal to 1,000,000 picofarads?
A. 0.001 microfarads B. 1 microfarad C. 1000 microfarads D. 1,000,000,000 microfarads
T5B09 (B)
Which decibel value most closely represents a power increase from 5 watts to 10 watts?
A. 2 dB B. 3 dB C. 5 dB D. 10 dB
T5B10 (C)
Which decibel value most closely represents a power decrease from 12 watts to 3 watts?
A. -1 dB B. -3 dB C. -6 dB D. -9 dB
T5C
Capacitance and inductance terminology and units; Radio frequency definition and units; Impedance definition and units; Calculating power
T5C01 (D)
What describes the ability to store energy in an electric field?
A. Inductance B. Resistance C. Tolerance D. Capacitance
T5C03 (D)
What describes the ability to store energy in a magnetic field?
A. Admittance B. Capacitance C. Resistance D. Inductance
T5C06 (A)
What does the abbreviation “RF” mean?
A. Radio frequency signals of all types B. The resonant frequency of a tuned circuit C. The real frequency transmitted as opposed to the apparent frequency D. Reflective force in antenna transmission lines
T5C08 (A)
What is the formula used to calculate electrical power (P) in a DC circuit?
A. P = I x E B. P = E / I C. P = E – I D. P = I + E
T5C09 (A)
How much power is delivered by a voltage of 13.8 volts DC and a current of 10 amperes?
A. 138 watts B. 0.7 watts C. 23.8 watts D. 3.8 watts
T5C10 (B)
How much power is delivered by a voltage of 12 volts DC and a current of 2.5 amperes?
A. 4.8 watts B. 30 watts C. 14.5 watts D. 0.208 watts
T5C11 (B)
How much current is required to deliver 120 watts at a voltage of 12 volts DC?
A. 0.1 amperes B. 10 amperes C. 12 amperes D. 132 amperes
T5D
Ohm’s Law; Series and parallel circuits
T5D01 (B)
What formula is used to calculate current in a circuit?
A. I = E x R B. I = E / R C. I = E + R D. I = E - R
T5D02 (A)
What formula is used to calculate voltage in a circuit?
A. E = I x R B. E = I / R C. E = I + R D. E = I - R
T5D03 (B)
What formula is used to calculate resistance in a circuit?
A. R = E x I B. R = E / I C. R = E + I D. R = E - I
T5D04 (B)
What is the resistance of a circuit in which a current of 3 amperes flows when connected to 90 volts?
A. 3 ohms B. 30 ohms C. 93 ohms D. 270 ohms
T5D05 (C)
What is the resistance of a circuit for which the applied voltage is 12 volts and the current flow is 1.5 amperes?
A. 18 ohms B. 0.125 ohms C. 8 ohms D. 13.5 ohms
T5D06 (A)
What is the resistance of a circuit that draws 4 amperes from a 12-volt source?
A. 3 ohms B. 16 ohms C. 48 ohms D. 8 ohms
T5D07 (D)
What is the current in a circuit with an applied voltage of 120 volts and a resistance of 80 ohms?
A. 9600 amperes B. 200 amperes C. 0.667 amperes D. 1.5 amperes
T5D08 (C)
What is the current through a 100-ohm resistor connected across 200 volts?
A. 20,000 amperes B. 0.5 amperes C. 2 amperes D. 100 amperes
T5D09 (C)
What is the current through a 24-ohm resistor connected across 240 volts?
A. 24,000 amperes B. 0.1 amperes C. 10 amperes D. 216 amperes
T5D10 (A)
What is the voltage across a 2-ohm resistor if a current of 0.5 amperes flows through it?
A. 1 volt B. 0.25 volts C. 2.5 volts D. 1.5 volts
T5D11 (B)
What is the voltage across a 10-ohm resistor if a current of 1 ampere flows through it?
A. 1 volt B. 10 volts C. 11 volts D. 9 volts
T5D12 (D)
What is the voltage across a 10-ohm resistor if a current of 2 amperes flows through it?
A. 8 volts B. 0.2 volts C. 12 volts D. 20 volts
SUBELEMENT T6 – ELECTRONIC AND ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
– [4 Exam Questions - 4 Groups]
T6A
Fixed and variable resistors; Capacitors; Inductors; Fuses; Switches; Batteries
T6A01 (B)
What electrical component opposes the flow of current in a DC circuit?
A. Inductor B. Resistor C. Inverter D. Transformer
T6A02 (C)
What type of component is often used as an adjustable volume control?
A. Fixed resistor B. Power resistor C. Potentiometer D. Transformer
T6A03 (B)
What electrical parameter is controlled by a potentiometer?
A. Inductance B. Resistance C. Capacitance D. Field strength
T6A04 (B)
What electrical component stores energy in an electric field?
A. Varistor B. Capacitor C. Inductor D. Diode
T6A05 (D)
What type of electrical component consists of conductive surfaces separated by an insulator?
A. Resistor B. Potentiometer C. Oscillator D. Capacitor
T6A06 (C)
What type of electrical component stores energy in a magnetic field?
A. Varistor B. Capacitor C. Inductor D. Diode
T6A07 (D)
What electrical component is typically constructed as a coil of wire?
A. Switch B. Capacitor C. Diode D. Inductor
T6A08 (C)
What is the function of an SPDT switch?
A. A single circuit is opened or closed B. Two circuits are opened or closed C. A single circuit is switched between one of two other circuits D. Two circuits are each switched between one of two other circuits
T6A09 (A)
What electrical component is used to protect other circuit components from current overloads?
A. Fuse B. Thyratron C. Varactor D. All these choices are correct
T6A10 (D)
Which of the following battery chemistries is rechargeable?
A. Nickel-metal hydride B. Lithium-ion C. Lead-acid D. All these choices are correct
T6A11 (B)
Which of the following battery chemistries is not rechargeable?
A. Nickel-cadmium B. Carbon-zinc C. Lead-acid D. Lithium-ion
T6A12 (A)
What type of switch is represented by component 3 in figure T-2?
A. Single-pole single-throw B. Single-pole double-throw C. Double-pole single-throw D. Double-pole double-throw
T6B
Semiconductors: basic principles and applications of solid state devices, diodes and transistors
T6B01 (A)
Which is true about forward voltage drop in a diode?
A. It is lower in some diode types than in others B. It is proportional to peak inverse voltage C. It indicates that the diode is defective D. It has no impact on the voltage delivered to the load
T6B02 (C)
What electronic component allows current to flow in only one direction?
A. Resistor B. Fuse C. Diode D. Driven element
T6B03 (C)
Which of these components can be used as an electronic switch?
A. Varistor B. Potentiometer C. Transistor D. Thermistor
T6B04 (B)
Which of the following components can consist of three regions of semiconductor material?
A. Alternator B. Transistor C. Triode D. Pentagrid converter
T6B05 (B)
What type of transistor has a gate, drain, and source?
A. Varistor B. Field-effect C. Tesla-effect D. Bipolar junction
T6B06 (B)
How is the cathode lead of a semiconductor diode often marked on the package?
A. With the word “cathode” B. With a stripe C. With the letter C D. With the letter K
T6B07 (A)
What causes a light-emitting diode (LED) to emit light?
A. Forward current B. Reverse current C. Capacitively-coupled RF signal D. Inductively-coupled RF signal
T6B08 (D)
What does the abbreviation FET stand for?
A. Frequency Emission Transmitter B. Fast Electron Transistor C. Free Electron Transmitter D. Field Effect Transistor
T6B09 (C)
What are the names for the electrodes of a diode?
A. Plus and minus B. Source and drain C. Anode and cathode D. Gate and base
T6B10 (B)
Which of the following can provide power gain?
A. Transformer B. Transistor C. Reactor D. Resistor
T6C
Circuit diagrams: use of schematics, basic structure; Schematic symbols of basic components
T6C01 (C)
What is the name of an electrical wiring diagram that uses standard component symbols?
A. Bill of materials B. Connector pinout C. Schematic D. Flow chart
T6C03 (B)
What is component 2 in figure T-1?
A. Resistor B. Transistor C. Indicator lamp D. Connector
T6C07 (D)
What is component 8 in figure T-2?
A. Resistor B. Inductor C. Regulator IC D. Light emitting diode
T6C08 (C)
What is component 9 in figure T-2?
A. Variable capacitor B. Variable inductor C. Variable resistor D. Variable transformer
T6C09 (D)
What is component 4 in figure T-2?
A. Variable inductor B. Double-pole switch C. Potentiometer D. Transformer
T6C10 (D)
What is component 3 in figure T-3?
A. Connector B. Meter C. Variable capacitor D. Variable inductor
T6D
Component functions: rectifiers, relays, voltage regulators, meters, indicators, integrated circuits, transformers; Resonant circuit; Shielding
T6D01 (B)
Which of the following devices or circuits changes an alternating current into a varying direct current signal?
A. Transformer B. Rectifier C. Amplifier D. Reflector
T6D02 (A)
What is a relay?
A. An electrically-controlled switch B. A current controlled amplifier C. An inverting amplifier D. A pass transistor
T6D03 (C)
Which of the following is a reason to use shielded wire?
A. To decrease the resistance of DC power connections B. To increase the current carrying capability of the wire C. To prevent coupling of unwanted signals to or from the wire D. To couple the wire to other signals
T6D04 (C)
Which of the following displays an electrical quantity as a numeric value?
A. Potentiometer B. Transistor C. Meter D. Relay
T6D05 (A)
What type of circuit controls the amount of voltage from a power supply?
A. Regulator B. Oscillator C. Filter D. Phase inverter
7.0.0.0.1 T6D06 (B) {- #}
What component changes 120 V AC power to a lower AC voltage for other uses?
A. Variable capacitor B. Transformer C. Transistor D. Diode
T6D07 (A)
Which of the following is commonly used as a visual indicator?
A. LED B. FET C. Zener diode D. Bipolar transistor
T6D08 (D)
Which of the following is combined with an inductor to make a resonant circuit?
A. Resistor B. Zener diode C. Potentiometer D. Capacitor
T6D09 (C)
What is the name of a device that combines several semiconductors and other components into one package?
A. Transducer B. Multi-pole relay C. Integrated circuit D. Transformer
T6D10 (C)
What is the function of component 2 in figure T-1?
A. Give off light when current flows through it B. Supply electrical energy C. Control the flow of current D. Convert electrical energy into radio waves
SUBELEMENT T7 – PRACTICAL CIRCUITS
– [4 Exam Questions - 4 Groups]
T7A
Station equipment: receivers, transceivers, transmitter amplifiers, receive amplifiers, transverters; Basic radio circuit concepts and terminology: sensitivity, selectivity, mixers, oscillators, PTT, modulation
T7A01 (B)
Which term describes the ability of a receiver to detect the presence of a signal?
A. Linearity B. Sensitivity C. Selectivity D. Total Harmonic Distortion
T7A02 (A)
What is a transceiver?
A. A device that combines a receiver and transmitter B. A device for matching feed line impedance to 50 ohms C. A device for automatically sending and decoding Morse code D. A device for converting receiver and transmitter frequencies to another band
T7A03 (B)
Which of the following is used to convert a signal from one frequency to another?
A. Phase splitter B. Mixer C. Inverter D. Amplifier
T7A04 (C)
Which term describes the ability of a receiver to discriminate between multiple signals?
A. Discrimination ratio B. Sensitivity C. Selectivity D. Harmonic distortion
T7A05 (D)
What is the name of a circuit that generates a signal at a specific frequency?
A. Reactance modulator B. Phase modulator C. Low-pass filter D. Oscillator
T7A06 (C)
What device converts the RF input and output of a transceiver to another band?
A. High-pass filter B. Low-pass filter C. Transverter D. Phase converter
T7A07 (B)
What is the function of a transceiver’s PTT input?
A. Input for a key used to send CW B. Switches transceiver from receive to transmit when grounded C. Provides a transmit tuning tone when grounded D. Input for a preamplifier tuning tone
T7A08 (C)
Which of the following describes combining speech with an RF carrier signal?
A. Impedance matching B. Oscillation C. Modulation D. Low-pass filtering
T7A09 (B)
What is the function of the SSB/CW-FM switch on a VHF power amplifier?
A. Change the mode of the transmitted signal B. Set the amplifier for proper operation in the selected mode C. Change the frequency range of the amplifier to operate in the proper segment of the band D. Reduce the received signal noise
T7B
Symptoms, causes, and cures of common transmitter and receiver problems: overload and overdrive, distortion, interference and consumer electronics, RF feedback
T7B01 (D)
What can you do if you are told your FM handheld or mobile transceiver is over-deviating?
A. Talk louder into the microphone B. Let the transceiver cool off C. Change to a higher power level D. Talk farther away from the microphone
T7B02 (A)
What would cause a broadcast AM or FM radio to receive an amateur radio transmission unintentionally?
A. The receiver is unable to reject strong signals outside the AM or FM band B. The microphone gain of the transmitter is turned up too high C. The audio amplifier of the transmitter is overloaded D. The deviation of an FM transmitter is set too low
T7B03 (D)
Which of the following can cause radio frequency interference?
A. Fundamental overload B. Harmonics C. Spurious emissions D. All these choices are correct
T7B04 (D)
Which of the following could you use to cure distorted audio caused by RF current on the shield of a microphone cable?
A. Band-pass filter B. Low-pass filter C. Preamplifier D. Ferrite choke
T7B05 (A)
How can fundamental overload of a non-amateur radio or TV receiver by an amateur signal be reduced or eliminated?
A. Block the amateur signal with a filter at the antenna input of the affected receiver B. Block the interfering signal with a filter on the amateur transmitter C. Switch the transmitter from FM to SSB D. Switch the transmitter to a narrow-band mode
T7B06 (A)
Which of the following actions should you take if a neighbor tells you that your station’s transmissions are interfering with their radio or TV reception?
A. Make sure that your station is functioning properly and that it does not cause interference to your own radio or television when it is tuned to the same channel B. Immediately turn off your transmitter and contact the nearest FCC office for assistance C. Install a harmonic doubler on the output of your transmitter and tune it until the interference is eliminated D. All these choices are correct
T7B07 (D)
Which of the following can reduce overload of a VHF transceiver by a nearby commercial FM station?
A. Installing an RF preamplifier B. Using double-shielded coaxial cable C. Installing bypass capacitors on the microphone cable D. Installing a band-reject filter
T7B08 (D)
What should you do if something in a neighbor’s home is causing harmful interference to your amateur station?
A. Work with your neighbor to identify the offending device B. Politely inform your neighbor that FCC rules prohibit the use of devices that cause interference C. Make sure your station meets the standards of good amateur practice D. All these choices are correct
T7B09 (D)
What should be the first step to resolve non-fiber optic cable TV interference caused by your amateur radio transmission?
A. Add a low-pass filter to the TV antenna input B. Add a high-pass filter to the TV antenna input C. Add a preamplifier to the TV antenna input D. Be sure all TV feed line coaxial connectors are installed properly
T7B10 (D)
What might be a problem if you receive a report that your audio signal through an FM repeater is distorted or unintelligible?
A. Your transmitter is slightly off frequency B. Your batteries are running low C. You are in a bad location D. All these choices are correct
T7B11 (C)
What is a symptom of RF feedback in a transmitter or transceiver?
A. Excessive SWR at the antenna connection B. The transmitter will not stay on the desired frequency C. Reports of garbled, distorted, or unintelligible voice transmissions D. Frequent blowing of power supply fuses
T7C
Antenna and transmission line measurements and troubleshooting: measuring SWR, effects of high SWR, causes of feed line failures; Basic coaxial cable characteristics; Use of dummy loads when testing
T7C01 (A)
What is the primary purpose of a dummy load?
A. To prevent transmitting signals over the air when making tests B. To prevent over-modulation of a transmitter C. To improve the efficiency of an antenna D. To improve the signal-to-noise ratio of a receiver
T7C02 (B)
Which of the following is used to determine if an antenna is resonant at the desired operating frequency?
A. A VTVM B. An antenna analyzer C. A Q meter D. A frequency counter
T7C03 (B)
What does a dummy load consist of?
A. A high-gain amplifier and a TR switch B. A non-inductive resistor mounted on a heat sink C. A low-voltage power supply and a DC relay D. A 50-ohm reactance used to terminate a transmission line
T7C04 (C)
What reading on an SWR meter indicates a perfect impedance match between the antenna and the feed line?
A. 50:50 B. Zero C. 1:1 D. Full Scale
T7C05 (A)
Why do most solid-state transmitters reduce output power as SWR increases beyond a certain level?
A. To protect the output amplifier transistors B. To comply with FCC rules on spectral purity C. Because power supplies cannot supply enough current at high SWR D. To lower the SWR on the transmission line
T7C06 (D)
What does an SWR reading of 4:1 indicate?
A. Loss of -4 dB B. Good impedance match C. Gain of +4 dB D. Impedance mismatch
T7C07 (C)
What happens to power lost in a feed line?
A. It increases the SWR B. It is radiated as harmonics C. It is converted into heat D. It distorts the signal
T7C08 (D)
Which instrument can be used to determine SWR?
A. Voltmeter B. Ohmmeter C. Iambic pentameter D. Directional wattmeter
T7C09 (A)
Which of the following causes failure of coaxial cables?
A. Moisture contamination B. Solder flux contamination C. Rapid fluctuation in transmitter output power D. Operation at 100% duty cycle for an extended period
T7C10 (D)
Why should the outer jacket of coaxial cable be resistant to ultraviolet light?
A. Ultraviolet resistant jackets prevent harmonic radiation B. Ultraviolet light can increase losses in the cable’s jacket C. Ultraviolet and RF signals can mix, causing interference D. Ultraviolet light can damage the jacket and allow water to enter the cable
T7C11 (C)
What is a disadvantage of air core coaxial cable when compared to foam or solid dielectric types?
A. It has more loss per foot B. It cannot be used for VHF or UHF antennas C. It requires special techniques to prevent moisture in the cable D. It cannot be used at below freezing temperatures
T7D
Using basic test instruments: voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter; Soldering ##### T7D01 (B) {- #T7D01}
Which instrument would you use to measure electric potential?
A. An ammeter B. A voltmeter C. A wavemeter D. An ohmmeter
T7D02 (B)
How is a voltmeter connected to a component to measure applied voltage?
A. In series B. In parallel C. In quadrature D. In phase
T7D03 (A)
When configured to measure current, how is a multimeter connected to a component?
A. In series B. In parallel C. In quadrature D. In phase
T7D04 (D)
Which instrument is used to measure electric current?
A. An ohmmeter B. An electrometer C. A voltmeter D. An ammeter
T7D06 (C)
Which of the following can damage a multimeter?
A. Attempting to measure resistance using the voltage setting B. Failing to connect one of the probes to ground C. Attempting to measure voltage when using the resistance setting D. Not allowing it to warm up properly
T7D07 (C)
Which of the following measurements are made using a multimeter?
A. Signal strength and noise B. Impedance and reactance C. Voltage and resistance D. All these choices are correct
T7D08 (A)
Which of the following types of solder should not be used for radio and electronic applications?
A. Acid-core solder B. Lead-tin solder C. Rosin-core solder D. Tin-copper solder
T7D09 (C)
What is the characteristic appearance of a cold tin-lead solder joint?
A. Dark black spots B. A bright or shiny surface C. A rough or lumpy surface D. Excessive solder
T7D10 (A)
What reading indicates that an ohmmeter is connected across a large, discharged capacitor?
A. Increasing resistance with time B. Decreasing resistance with time C. Steady full-scale reading D. Alternating between open and short circuit
T7D11 (B)
Which of the following precautions should be taken when measuring in-circuit resistance with an ohmmeter?
A. Ensure that the applied voltages are correct B. Ensure that the circuit is not powered C. Ensure that the circuit is grounded D. Ensure that the circuit is operating at the correct frequency
SUBELEMENT T8 – SIGNALS AND EMISSIONS
– [4 Exam Questions - 4 Groups]
T8A
Basic characteristics of FM and SSB; Bandwidth of various modulation modes: CW, SSB, FM, fast-scan TV; Choice of emission type: selection of USB vs LSB, use of SSB for weak signal work, use of FM for VHF packet and repeaters
T8A01 (C)
Which of the following is a form of amplitude modulation?
A. Spread spectrum B. Packet radio C. Single sideband D. Phase shift keying (PSK)
T8A03 (C)
Which type of voice mode is often used for long-distance (weak signal) contacts on the VHF and UHF bands?
A. FM B. DRM C. SSB D. PM
T8A06 (A)
Which sideband is normally used for 10 meter HF, VHF, and UHF single-sideband communications?
A. Upper sideband B. Lower sideband C. Suppressed sideband D. Inverted sideband
T8A07 (C)
What is a characteristic of single sideband (SSB) compared to FM?
A. SSB signals are easier to tune in correctly B. SSB signals are less susceptible to interference C. SSB signals have narrower bandwidth D. All these choices are correct
T8A08 (B)
What is the approximate bandwidth of a typical single sideband (SSB) voice signal?
A. 1 kHz B. 3 kHz C. 6 kHz D. 15 kHz
T8A09 (C)
What is the approximate bandwidth of a VHF repeater FM voice signal?
A. Less than 500 Hz B. About 150 kHz C. Between 10 and 15 kHz D. Between 50 and 125 kHz
T8A10 (B)
What is the approximate bandwidth of AM fast-scan TV transmissions?
A. More than 10 MHz B. About 6 MHz C. About 3 MHz D. About 1 MHz
T8A11 (B)
What is the approximate bandwidth required to transmit a CW signal?
A. 2.4 kHz B. 150 Hz C. 1000 Hz D. 15 kHz
T8B
Amateur satellite operation: Doppler shift, basic orbits, operating protocols, modulation mode selection, transmitter power considerations, telemetry and telecommand, satellite tracking programs, beacons, uplink and downlink mode definitions, spin fading, definition of “LEO”, setting uplink power
T8B01 (C)
What telemetry information is typically transmitted by satellite beacons?
A. The signal strength of received signals B. Time of day accurate to plus or minus 1/10 second C. Health and status of the satellite D. All these choices are correct
T8B02 (B)
What is the impact of using excessive effective radiated power on a satellite uplink?
A. Possibility of commanding the satellite to an improper mode B. Blocking access by other users C. Overloading the satellite batteries D. Possibility of rebooting the satellite control computer
T8B03 (D)
Which of the following are provided by satellite tracking programs?
A. Maps showing the real-time position of the satellite track over Earth B. The time, azimuth, and elevation of the start, maximum altitude, and end of a pass C. The apparent frequency of the satellite transmission, including effects of Doppler shift D. All these choices are correct
T8B05 (D)
What is a satellite beacon?
A. The primary transmit antenna on the satellite B. An indicator light that shows where to point your antenna C. A reflective surface on the satellite D. A transmission from a satellite that contains status information
T8B06 (B)
Which of the following are inputs to a satellite tracking program?
A. The satellite transmitted power B. The Keplerian elements C. The last observed time of zero Doppler shift D. All these choices are correct
T8B07 (C)
What is Doppler shift in reference to satellite communications?
A. A change in the satellite orbit B. A mode where the satellite receives signals on one band and transmits on another C. An observed change in signal frequency caused by relative motion between the satellite and Earth station D. A special digital communications mode for some satellites
T8B08 (B)
What is meant by the statement that a satellite is operating in U/V mode?
A. The satellite uplink is in the 15 meter band and the downlink is in the 10 meter band B. The satellite uplink is in the 70 centimeter band and the downlink is in the 2 meter band C. The satellite operates using ultraviolet frequencies D. The satellite frequencies are usually variable
T8B09 (B)
What causes spin fading of satellite signals?
A. Circular polarized noise interference radiated from the sun B. Rotation of the satellite and its antennas C. Doppler shift of the received signal D. Interfering signals within the satellite uplink band
T8B10 (D)
What is a LEO satellite?
A. A sun synchronous satellite B. A highly elliptical orbit satellite C. A satellite in low energy operation mode D. A satellite in low earth orbit
T8B11 (A)
Who may receive telemetry from a space station?
A. Anyone B. A licensed radio amateur with a transmitter equipped for interrogating the satellite C. A licensed radio amateur who has been certified by the protocol developer D. A licensed radio amateur who has registered for an access code from AMSAT
T8B12 (C)
Which of the following is a way to determine whether your satellite uplink power is neither too low nor too high?
A. Check your signal strength report in the telemetry data B. Listen for distortion on your downlink signal C. Your signal strength on the downlink should be about the same as the beacon D. All these choices are correct
T8C
Operating activities: radio direction finding, contests, linking over the internet, exchanging grid locators
T8C01 (C)
Which of the following methods is used to locate sources of noise interference or jamming?
A. Echolocation B. Doppler radar C. Radio direction finding D. Phase locking
T8C02 (B)
Which of these items would be useful for a hidden transmitter hunt?
A. Calibrated SWR meter B. A directional antenna C. A calibrated noise bridge D. All these choices are correct
T8C03 (D)
What operating activity involves contacting as many stations as possible during a specified period?
A. Simulated emergency exercises B. Net operations C. Public service events D. Contesting
T8C04 (C)
Which of the following is good procedure when contacting another station in a contest?
A. Sign only the last two letters of your call if there are many other stations calling B. Contact the station twice to be sure that you are in his log C. Send only the minimum information needed for proper identification and the contest exchange D. All these choices are correct
T8C05 (A)
What is a grid locator?
A. A letter-number designator assigned to a geographic location B. A letter-number designator assigned to an azimuth and elevation C. An instrument for neutralizing a final amplifier D. An instrument for radio direction finding
7.0.0.0.2 T8C06 (D) (#BT8C05)
How is over the air access to IRLP nodes accomplished?
A. By obtaining a password that is sent via voice to the node B. By using DTMF signals C. By entering the proper internet password D. By using CTCSS tone codes
T8C07 (D)
What is Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP)?
A. A set of rules specifying how to identify your station when linked over the internet to another station B. A technique employed to “spot” DX stations via the internet C. A technique for measuring the modulation quality of a transmitter using remote sites monitored via the internet D. A method of delivering voice communications over the internet using digital techniques
T8C08 (A)
What is the Internet Radio Linking Project (IRLP)?
A. A technique to connect amateur radio systems, such as repeaters, via the internet using Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) B. A system for providing access to websites via amateur radio C. A system for informing amateurs in real time of the frequency of active DX stations D. A technique for measuring signal strength of an amateur transmitter via the internet
T8C09 (D)
Which of the following protocols enables an amateur station to transmit through a repeater without using a radio to initiate the transmission?
T8D
Non-voice and digital communications: image signals and definition of NTSC, CW, packet radio, PSK, APRS, error detection and correction, amateur radio networking, Digital Mobile Radio, WSJT modes, Broadband-Hamnet
T8D01 (D)
Which of the following is a digital communications mode?
A. Packet radio B. IEEE 802.11 C. FT8 D. All these choices are correct
T8D02 (B)
What is a “talkgroup” on a DMR repeater?
A. A group of operators sharing common interests B. A way for groups of users to share a channel at different times without hearing other users on the channel C. A protocol that increases the signal-to-noise ratio when multiple repeaters are linked together D. A net that meets at a specified time
T8D03 (D)
What kind of data can be transmitted by APRS?
A. GPS position data B. Text messages C. Weather data D. All these choices are correct
T8D04 (C)
What type of transmission is indicated by the term “NTSC?”
A. A Normal Transmission mode in Static Circuit B. A special mode for satellite uplink C. An analog fast-scan color TV signal D. A frame compression scheme for TV signals
T8D05 (A)
Which of the following is an application of APRS?
A. Providing real-time tactical digital communications in conjunction with a map showing the locations of stations B. Showing automatically the number of packets transmitted via PACTOR during a specific time interval C. Providing voice over internet connection between repeaters D. Providing information on the number of stations signed into a repeater
T8D06 (B)
What does the abbreviation “PSK” mean?
A. Pulse Shift Keying B. Phase Shift Keying C. Packet Short Keying D. Phased Slide Keying
T8D07 (A)
Which of the following describes DMR?
A. A technique for time-multiplexing two digital voice signals on a single 12.5 kHz repeater channel B. An automatic position tracking mode for FM mobiles communicating through repeaters C. An automatic computer logging technique for hands-off logging when communicating while operating a vehicle D. A digital technique for transmitting on two repeater inputs simultaneously for automatic error correction
T8D08 (D)
Which of the following is included in packet radio transmissions?
A. A check sum that permits error detection B. A header that contains the call sign of the station to which the information is being sent C. Automatic repeat request in case of error D. All these choices are correct
T8D09 (D)
What is CW?
A. A type of electromagnetic propagation B. A digital mode used primarily on 2 meter FM C. A technique for coil winding D. Another name for a Morse code transmission
T8D10 (D)
Which of the following operating activities is supported by digital mode software in the WSJT-X software suite?
A. Earth-Moon-Earth B. Weak signal propagation beacons C. Meteor scatter D. All these choices are correct
T8D11 (C)
What is an ARQ transmission system?
A. A special transmission format limited to video signals B. A system used to encrypt command signals to an amateur radio satellite C. An error correction method in which the receiving station detects errors and sends a request for retransmission D. A method of compressing data using autonomous reiterative Q codes prior to final encoding
T8D12 (A)
Which of the following best describes an amateur radio mesh network?
A. An amateur-radio based data network using commercial Wi-Fi equipment with modified firmware B. A wide-bandwidth digital voice mode employing DMR protocols C. A satellite communications network using modified commercial satellite TV hardware D. An internet linking protocol used to network repeaters
SUBELEMENT T9 – ANTENNAS AND FEED LINES
- [2 Exam Questions - 2 Groups]
T9A
Antennas: vertical and horizontal polarization, concept of antenna gain, definition and types of beam antennas, antenna loading, common portable and mobile antennas, relationships between resonant length and frequency, dipole pattern
T9A01 (C)
What is a beam antenna?
A. An antenna built from aluminum I-beams B. An omnidirectional antenna invented by Clarence Beam C. An antenna that concentrates signals in one direction D. An antenna that reverses the phase of received signals
T9A02 (A)
Which of the following describes a type of antenna loading?
A. Electrically lengthening by inserting inductors in radiating elements B. Inserting a resistor in the radiating portion of the antenna to make it resonant C. Installing a spring in the base of a mobile vertical antenna to make it more flexible D. Strengthening the radiating elements of a beam antenna to better resist wind damage
T9A03 (B)
Which of the following describes a simple dipole oriented parallel to Earth’s surface?
A. A ground-wave antenna B. A horizontally polarized antenna C. A travelling-wave antenna D. A vertically polarized antenna
T9A04 (A)
What is a disadvantage of the short, flexible antenna supplied with most handheld radio transceivers, compared to a full-sized quarter-wave antenna?
A. It has low efficiency B. It transmits only circularly polarized signals C. It is mechanically fragile D. All these choices are correct
T9A05 (C)
Which of the following increases the resonant frequency of a dipole antenna?
A. Lengthening it B. Inserting coils in series with radiating wires C. Shortening it D. Adding capacitive loading to the ends of the radiating wires
T9A06 (D)
Which of the following types of antenna offers the greatest gain?
A. 5/8 wave vertical B. Isotropic C. J pole D. Yagi
T9A07 (A)
What is a disadvantage of using a handheld VHF transceiver with a flexible antenna inside a vehicle?
A. Signal strength is reduced due to the shielding effect of the vehicle B. The bandwidth of the antenna will decrease, increasing SWR C. The SWR might decrease, decreasing the signal strength D. All these choices are correct
T9A08 (C)
What is the approximate length, in inches, of a quarter-wavelength vertical antenna for 146 MHz?
A. 112 B. 50 C. 19 D. 12
T9A09 (C)
What is the approximate length, in inches, of a half-wavelength 6 meter dipole antenna?
A. 6 B. 50 C. 112 D. 236
T9A10 (D)
In which direction does a half-wave dipole antenna radiate the strongest signal?
A. Equally in all directions B. Off the ends of the antenna C. In the direction of the feed line D. Broadside to the antenna
T9A11 (C)
What is antenna gain?
A. The additional power that is added to the transmitter power B. The additional power that is required in the antenna when transmitting on a higher frequency C. The increase in signal strength in a specified direction compared to a reference antenna D. The increase in impedance on receive or transmit compared to a reference antenna
T9B
Feed lines: types, attenuation vs frequency, selecting; SWR concepts; Antenna tuners (couplers); RF Connectors: selecting, weather protection
T9B01 (B)
What is a benefit of low SWR?
A. Reduced television interference B. Reduced signal loss C. Less antenna wear D. All these choices are correct
T9B02 (B)
What is the most common impedance of coaxial cables used in amateur radio?
A. 8 ohms B. 50 ohms C. 600 ohms D. 12 ohms
T9B03 (A)
Why is coaxial cable the most common feed line for amateur radio antenna systems?
A. It is easy to use and requires few special installation considerations B. It has less loss than any other type of feed line C. It can handle more power than any other type of feed line D. It is less expensive than any other type of feed line
T9B04 (A)
What is the major function of an antenna tuner (antenna coupler)?
A. It matches the antenna system impedance to the transceiver’s output impedance B. It helps a receiver automatically tune in weak stations C. It allows an antenna to be used on both transmit and receive D. It automatically selects the proper antenna for the frequency band being used
T9B05 (D)
What happens as the frequency of a signal in coaxial cable is increased?
A. The characteristic impedance decreases B. The loss decreases C. The characteristic impedance increases D. The loss increases
T9B07 (C)
Which of the following is true of PL-259 type coax connectors?
A. They are preferred for microwave operation B. They are watertight C. They are commonly used at HF and VHF frequencies D. They are a bayonet-type connector
T9B08 (D)
Which of the following is a source of loss in coaxial feed line?
A. Water intrusion into coaxial connectors B. High SWR C. Multiple connectors in the line D. All these choices are correct
T9B09 (B)
What can cause erratic changes in SWR?
A. Local thunderstorm B. Loose connection in the antenna or feed line C. Over-modulation D. Overload from a strong local station
T9B10 (C)
What is the electrical difference between RG-58 and RG-213 coaxial cable?
A. There is no significant difference between the two types B. RG-58 cable has two shields C. RG-213 cable has less loss at a given frequency D. RG-58 cable can handle higher power levels
T9B11 (C)
Which of the following types of feed line has the lowest loss at VHF and UHF?
A. 50-ohm flexible coax B. Multi-conductor unbalanced cable C. Air-insulated hardline D. 75-ohm flexible coax
T9B12 (A)
What is standing wave ratio (SWR)?
A. A measure of how well a load is matched to a transmission line B. The ratio of amplifier power output to input C. The transmitter efficiency ratio D. An indication of the quality of your station’s ground connection
SUBELEMENT T0 – SAFETY
– [3 Exam Questions - 3 Groups]
T0A
Power circuits and hazards: hazardous voltages, fuses and circuit breakers, grounding, electrical code compliance; Lightning protection; Battery safety
T0A01 (B)
Which of the following is a safety hazard of a 12-volt storage battery?
A. Touching both terminals with the hands can cause electrical shock B. Shorting the terminals can cause burns, fire, or an explosion C. RF emissions from a nearby transmitter can cause the electrolyte to emit poison gas D. All these choices are correct
T0A02 (D)
What health hazard is presented by electrical current flowing through the body?
A. It may cause injury by heating tissue B. It may disrupt the electrical functions of cells C. It may cause involuntary muscle contractions D. All these choices are correct
T0A03 (B)
In the United States, what circuit does black wire insulation indicate in a three-wire 120 V cable?
A. Neutral B. Hot C. Equipment ground D. Black insulation is never used
T0A04 (B)
What is the purpose of a fuse in an electrical circuit?
A. To prevent power supply ripple from damaging a component B. To remove power in case of overload C. To limit current to prevent shocks D. All these choices are correct
T0A05 (C)
Why should a 5-ampere fuse never be replaced with a 20-ampere fuse?
A. The larger fuse would be likely to blow because it is rated for higher current B. The power supply ripple would greatly increase C. Excessive current could cause a fire D. All these choices are correct
T0A06 (D)
What is a good way to guard against electrical shock at your station?
A. Use three-wire cords and plugs for all AC powered equipment B. Connect all AC powered station equipment to a common safety ground C. Install mechanical interlocks in high-voltage circuits D. All these choices are correct
T0A07 (D)
Where should a lightning arrester be installed in a coaxial feed line?
A. At the output connector of a transceiver B. At the antenna feed point C. At the AC power service panel D. On a grounded panel near where feed lines enter the building
T0A08 (A)
Where should a fuse or circuit breaker be installed in a 120V AC power circuit?
A. In series with the hot conductor only B. In series with the hot and neutral conductors C. In parallel with the hot conductor only D. In parallel with the hot and neutral conductors
T0A09 (C)
What should be done to all external ground rods or earth connections?
A. Waterproof them with silicone caulk or electrical tape B. Keep them as far apart as possible C. Bond them together with heavy wire or conductive strap D. Tune them for resonance on the lowest frequency of operation
T0A10 (A)
What hazard is caused by charging or discharging a battery too quickly?
A. Overheating or out-gassing B. Excess output ripple C. Half-wave rectification D. Inverse memory effect
T0A11 (D)
What hazard exists in a power supply immediately after turning it off?
A. Circulating currents in the DC filter B. Leakage flux in the power transformer C. Voltage transients from kickback diodes D. Charge stored in filter capacitors
T0A12 (B)
Which of the following precautions should be taken when measuring high voltages with a voltmeter?
A. Ensure that the voltmeter has very low impedance B. Ensure that the voltmeter and leads are rated for use at the voltages to be measured C. Ensure that the circuit is grounded through the voltmeter D. Ensure that the voltmeter is set to the correct frequency
T0B
Antenna safety: tower safety and grounding, installing antennas, antenna supports
T0B01 (C)
Which of the following is good practice when installing ground wires on a tower for lightning protection?
A. Put a drip loop in the ground connection to prevent water damage to the ground system B. Make sure all ground wire bends are right angles C. Ensure that connections are short and direct D. All these choices are correct
T0B02 (D)
What is required when climbing an antenna tower?
A. Have sufficient training on safe tower climbing techniques B. Use appropriate tie-off to the tower at all times C. Always wear an approved climbing harness D. All these choices are correct
T0B03 (D)
Under what circumstances is it safe to climb a tower without a helper or observer?
A. When no electrical work is being performed B. When no mechanical work is being performed C. When the work being done is not more than 20 feet above the ground D. Never
T0B04 (C)
Which of the following is an important safety precaution to observe when putting up an antenna tower?
A. Wear a ground strap connected to your wrist at all times B. Insulate the base of the tower to avoid lightning strikes C. Look for and stay clear of any overhead electrical wires D. All these choices are correct
T0B05 (B)
What is the purpose of a safety wire through a turnbuckle used to tension guy lines?
A. Secure the guy line if the turnbuckle breaks B. Prevent loosening of the turnbuckle from vibration C. Provide a ground path for lightning strikes D. Provide an ability to measure for proper tensioning
T0B06 (D)
What is the minimum safe distance from a power line to allow when installing an antenna?
A. Add the height of the antenna to the height of the power line and multiply by a factor of 1.5 B. The height of the power line above ground C. 1/2 wavelength at the operating frequency D. Enough so that if the antenna falls, no part of it can come closer than 10 feet to the power wires
T0B07 (C)
Which of the following is an important safety rule to remember when using a crank-up tower?
A. This type of tower must never be painted B. This type of tower must never be grounded C. This type of tower must not be climbed unless it is retracted, or mechanical safety locking devices have been installed D. All these choices are correct
T0B08 (D)
Which is a proper grounding method for a tower?
A. A single four-foot ground rod, driven into the ground no more than 12 inches from the base B. A ferrite-core RF choke connected between the tower and ground C. A connection between the tower base and a cold water pipe D. Separate eight-foot ground rods for each tower leg, bonded to the tower and each other
T0B09 (C)
Why should you avoid attaching an antenna to a utility pole?
A. The antenna will not work properly because of induced voltages B. The 60 Hz radiations from the feed line may increase the SWR C. The antenna could contact high-voltage power lines D. All these choices are correct
T0C
RF hazards: radiation exposure, proximity to antennas, recognized safe power levels, radiation types, duty cycle
T0C01 (D)
What type of radiation are radio signals?
A. Gamma radiation B. Ionizing radiation C. Alpha radiation D. Non-ionizing radiation
T0C02 (B)
At which of the following frequencies does maximum permissible exposure have the lowest value?
A. 3.5 MHz B. 50 MHz C. 440 MHz D. 1296 MHz
T0C03 (C)
How does the allowable power density for RF safety change if duty cycle changes from 100 percent to 50 percent?
A. It increases by a factor of 3 B. It decreases by 50 percent C. It increases by a factor of 2 D. There is no adjustment allowed for lower duty cycle
T0C04 (D)
What factors affect the RF exposure of people near an amateur station antenna?
A. Frequency and power level of the RF field B. Distance from the antenna to a person C. Radiation pattern of the antenna D. All these choices are correct
T0C05 (D)
Why do exposure limits vary with frequency?
A. Lower frequency RF fields have more energy than higher frequency fields B. Lower frequency RF fields do not penetrate the human body C. Higher frequency RF fields are transient in nature D. The human body absorbs more RF energy at some frequencies than at others
T0C06 (D)
Which of the following is an acceptable method to determine whether your station complies with FCC RF exposure regulations?
A. By calculation based on FCC OET Bulletin 65 B. By calculation based on computer modeling C. By measurement of field strength using calibrated equipment D. All these choices are correct
T0C07 (B)
What hazard is created by touching an antenna during a transmission?
A. Electrocution B. RF burn to skin C. Radiation poisoning D. All these choices are correct
T0C08 (A)
Which of the following actions can reduce exposure to RF radiation?
A. Relocate antennas B. Relocate the transmitter C. Increase the duty cycle D. All these choices are correct
T0C09 (B)
How can you make sure your station stays in compliance with RF safety regulations?
A. By informing the FCC of any changes made in your station B. By re-evaluating the station whenever an item in the transmitter or antenna system is changed C. By making sure your antennas have low SWR D. All these choices are correct
T0C10 (A)
Why is duty cycle one of the factors used to determine safe RF radiation exposure levels?
A. It affects the average exposure to radiation B. It affects the peak exposure to radiation C. It takes into account the antenna feed line loss D. It takes into account the thermal effects of the final amplifier
T0C11 (C)
What is the definition of duty cycle during the averaging time for RF exposure?
A. The difference between the lowest power output and the highest power output of a transmitter B. The difference between the PEP and average power output of a transmitter C. The percentage of time that a transmitter is transmitting D. The percentage of time that a transmitter is not transmitting
T0C12 (A)
How does RF radiation differ from ionizing radiation (radioactivity)?
A. RF radiation does not have sufficient energy to cause chemical changes in cells and damage DNA B. RF radiation can only be detected with an RF dosimeter C. RF radiation is limited in range to a few feet D. RF radiation is perfectly safe
Figures
T-1
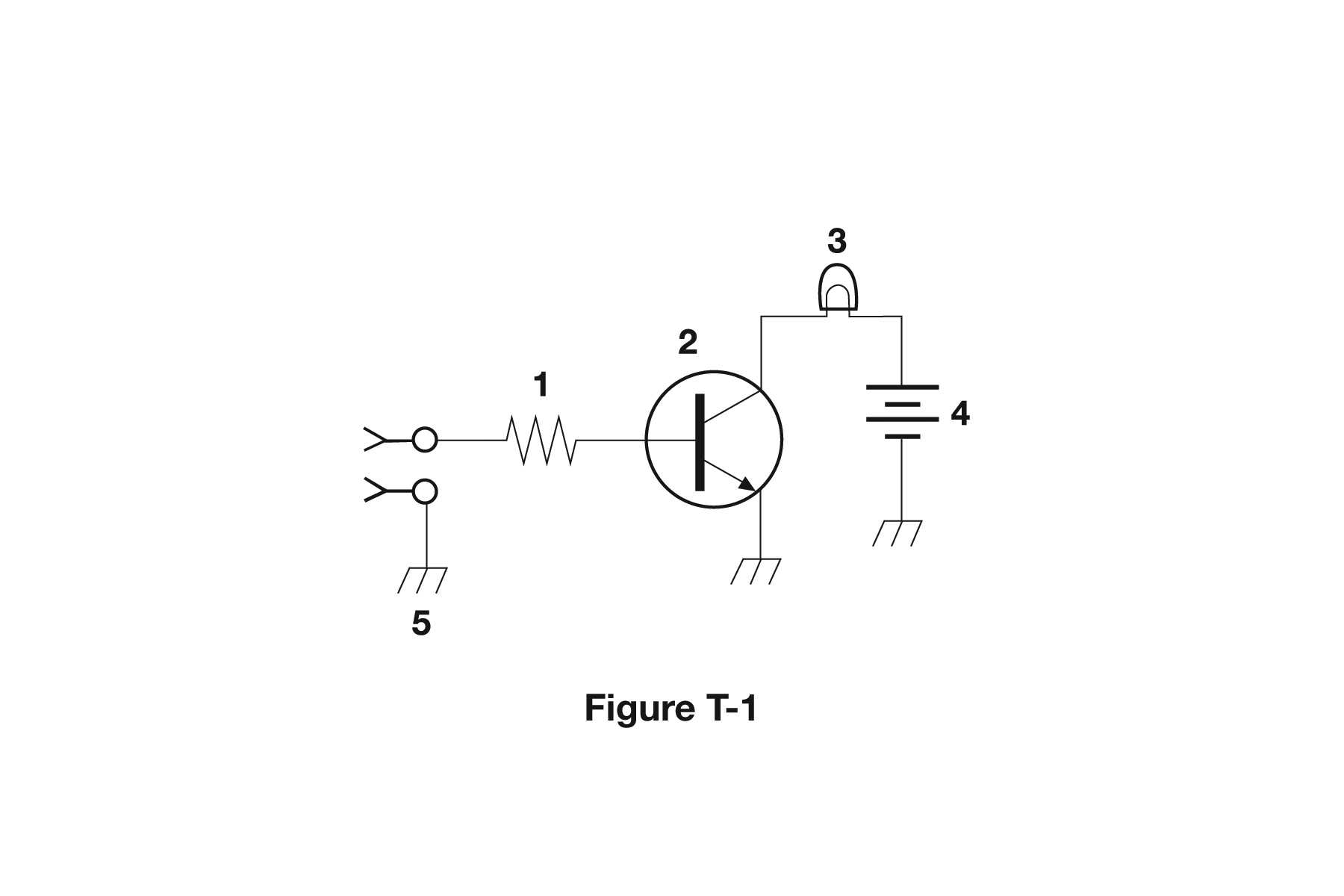
Figure 7.1: T-1 from http://ncvec.org/downloads/T1.jpg
T-2
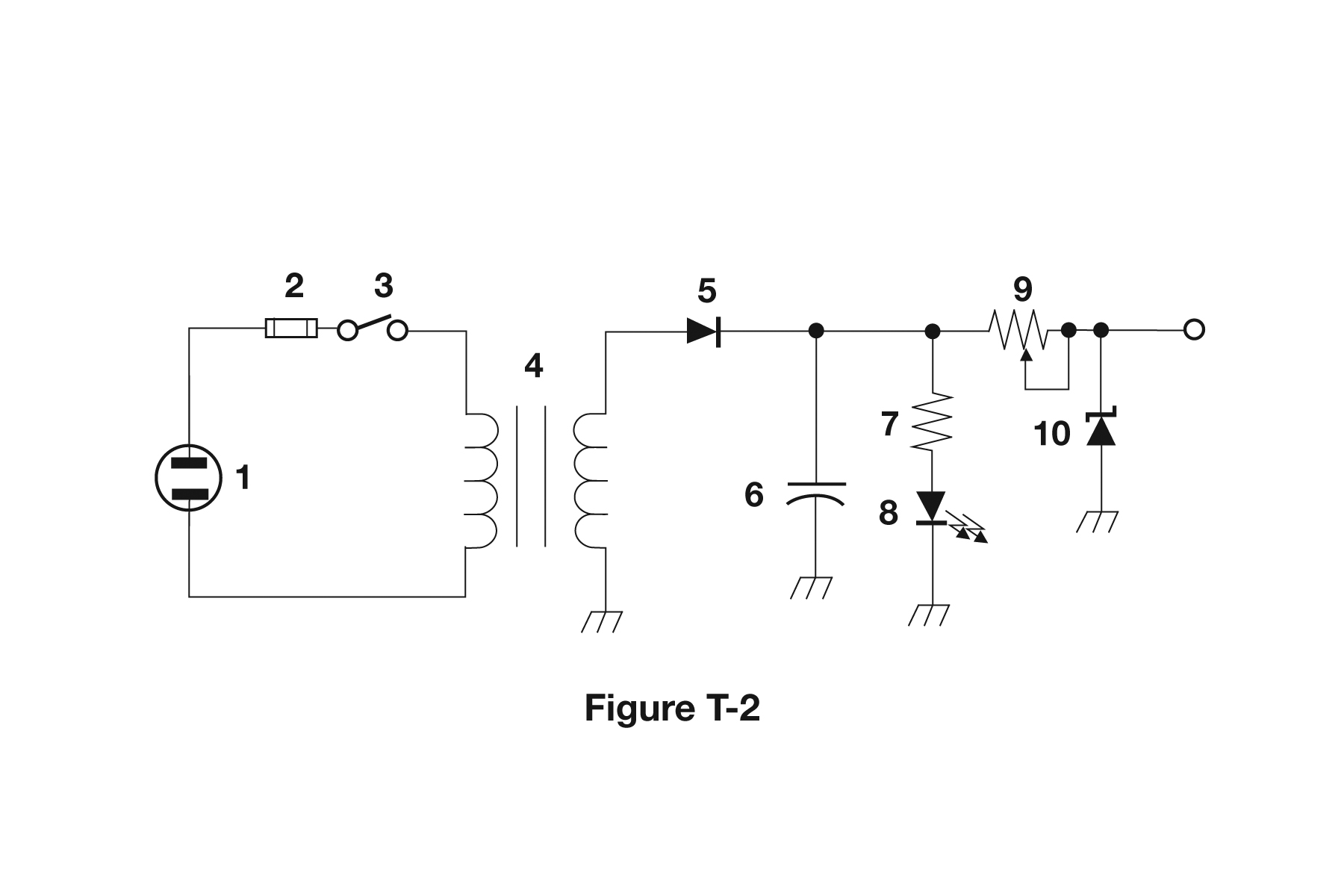
Figure 7.2: T-2 from http://ncvec.org/downloads/T2.jpg
T-3
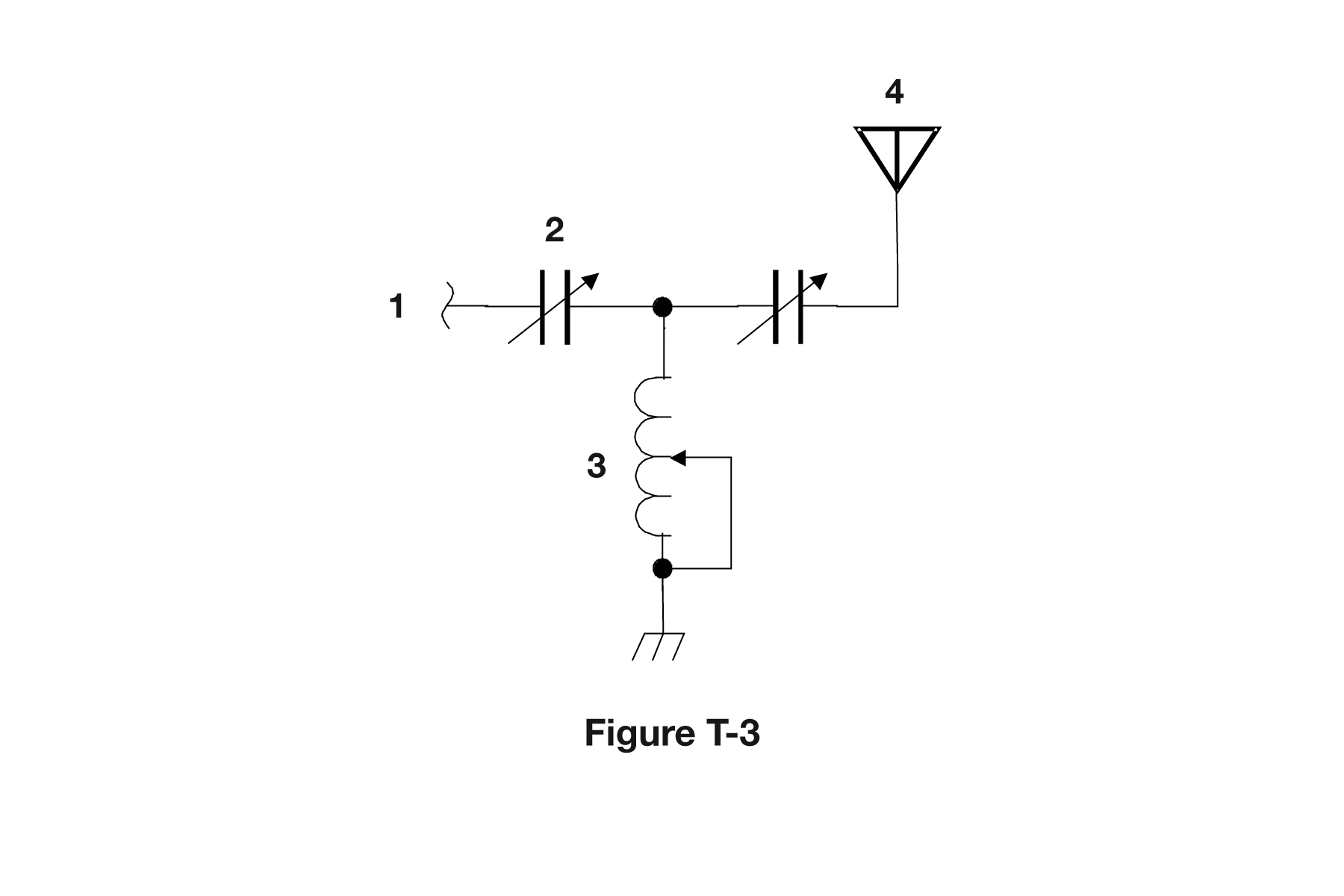
Figure 7.3: T-3 from http://ncvec.org/downloads/T3.jpg